Aug 28, 2020-The Science…This new study, by ENIGMA researchers, examined the newly-defined superphylum Patescibacteria, finding that they have developed unique characteristics which help adapt themselves to nutrient-limited but stable conditions in groundwater. Characteristics include highly reduced genome sizes and ultra-small cell size with simplified metabolism pathways for energy and carbon utilization as well as basic systems for DNA replication and translation essential for growth and reproduction. Meanwhile, they lack numerous nonessential functions related to motility, chemotaxis, outer membrane function, polysaccharide metabolism, etc. They also lack CRISPR-mediated phage defense, considered the most important mechanism of bacterial immunity; while possessing alternative strategies for phage resistance.
News Articles Archives
EISA-MRM: Quantitative MS Toward A $5 Metabolome
August 24, 2020-Xue J, Guijas C, Benton HP, Warth B, Siuzdak G (2020) METLIN MS2 molecular standards database: a broad chemical and biological resource. Nature Methods. 17(10) 953-954 [doi]: 10.1038/s41592-020-0942-5, PMID: 32839599
SCIENCE: A key ENIGMA Aim is linking field data to the phenotypic characterization of isolates, testing mechanistic hypothesis in the laboratory.
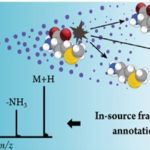
EISA-MRM (Enhanced In-Source Fragmentation/Annotation Multiple Reaction Monitoring):
This novel quantitative mass spectrometry technique allows the measurement of concentrations of the metabolites in ENIGMA samples using much cheaper instrumentation. These efforts characterizing key metabolites developing experimental quantitative methods to monitor the change of metabolome in bacteria are mission critical. The techniques will be used to design and test field-derived hypothesis in the laboratory.
Selective carbon sources influence the end-products of microbial nitrate respiration
July 21, 2020-Carlson, H.K.; L.M. Lui, M.N. Price, A.E. Kazakov, A.V. Carr, J.V. Kuehl, T.K. Owens, T. Nielsen, A.P. Arkin, A.M. Deutschbauer (2020) Selective carbon sources influence the end-products of microbial nitrate respiration. International Society for Microbial Ecology Journal. [doi]:10.1038/s41396-020-0666-7
The world’s population relies on nitrogen fertilizer to maintain productive agricultural ecosystems. However, as a consequence of industrial fertilizer use the nitrogen cycle has become the most anthropogenically perturbed element cycle, and nitrogen contamination of surface waters and groundwater has serious consequences for public and environmental health. For example, nitrate in water supplies can cause methemoglobinemia, nitrate in coastal waters leads to eutrophication, and incomplete denitrification drives the accumulation of nitrous oxide, a potent greenhouse gas.
GapMind: Folate-independent Methionine Synthases
Jun 23, 2020-Diverse bacteria and archaea rely on unusual methionine synthases. The Science…Methionine is one of the amino acids that make up proteins, and the final step in methionine synthesis is the transfer of a methyl group. Usually, the methyl group is obtained from methyl folates, but some anaerobic microbes use vitamin B12-binding proteins instead. By analyzing the genomes of diverse bacteria and archaea, we identified four families of folate-independent methionine synthases. Three of these families co-occur with B12-binding proteins, which indicates their likely partners. The fourth family does not require vitamin B12; instead, it obtains methyl groups from an oxygen-dependent partner protein.
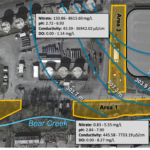
Setting The Stage For Ongoing Geochemical/Geophysical Characterization of ENIGMA Field Site
May 12, 2020-Characterization of subsurface media from locations up- and down-gradient of a uranium-contaminated aquifer
Moon, J.-W., Paradis, C.J., Joyner, D.C., von Netzer, F., Majumder, E.L.,Dixon, E.R., Podar, M., Ge, X., Walian, P.J., Smith, H.J., Wu, X., Zane, G.M., Walker, K.F., Thorgersen,M.P., Poole II, , F.L., Lui, L.M., Adams, B.G., De León, K.B., Brewer, S.S., Williams, D.E., Lowe, K.A.,Rodriguez Jr., , M., Mehlhorn, T.L., Pfiffner, S.M., Chakraborty, R., Arkin, A.P., Wall, J.D., Fields, M.W.,Adams, M.W.W., Stahl, D.A., Elias, D.A., Hazen, T.C.
Chemosphere, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.126951
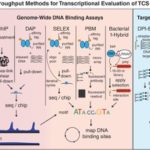
Review of ENIGMA tools Proposes New Use for DAP-chip
April 5, 2020-Tools to map target genes of bacterial two-component system response regulators
Rajeev L, Garber ME, Mukhopadhyay, A
Environmental Microbiology Reports. 2020 doi.org/10.1111/1758-2229.12838
Microbial signaling and gene regulation is an important aspect of the ecology being studied by the ENIGMA project at the Oakridge Field Site.
There are several methods currently available to examine transcriptionally acting signaling systems in bacteria. Approaches such as DAP-seq, an emerging method, have their origins in the DAP-chip approach, a legacy of earlier ENIGMA studies. Here we showcase DAP-chip, which was used to examine all two-component signaling systems in the model sulfate reducer, Desulfovibrio vulgaris. Recently, DAP-seq was used to examine Cu and Zn regulating systems in the P. stutzeri.
Assessing and Predicting Ability and Rate of Contaminant Immobilization by Bacteria
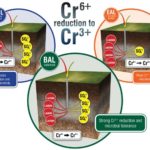
Franco, L.C.; S. Steinbeisser, G.M. Zane, J.D. Wall, and M.W. Fields. 2018. Cr(VI) reduction and physiological toxicity are impacted by resource ratio in Desulfovibrio vulgaris. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 102:2839-2850 [doi]:1007/s00253-017-8724-4 {PMID}:29429007 PMCID:PMC5847207 OSTI:1420176 The presented study shows that resource ratio at different temperature has profound impacts on Cr(VI) reduction rates and Cr(VI) tolerance in Desulfovibrio vulgaris, […]
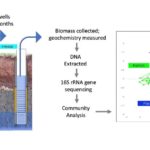
Characterizing Bacterial Diversity With Respect To Hydrochemistry
Zelaya, A.; A. Parker, K.L. Bailey, P. Zhang, J. Van Nostrand, D. Ning, D.A. Elias, J. Zhou, T.C Hazen, A.P Arkin and M.W. Fields (2019) High spatiotemporal variability of bacterial diversity over short time scales with unique hydrochemical associations within a shallow aquifer. Water Research. [doi]:1016/j.watres.2019.114917{PMID}:31387058 OSTI:1607016
Nov 5, 2019 -Freshwater resources are becoming jeopardized at alarming rates. Full assessment of uncontaminated groundwater composition, both biotic and abiotic components, over space and time is necessary to establish expected variability over both short- and long-term scales.