###How to predict a protein’s function or a bacterium’s capabilities
Predicting what a bacterium can do from its genome is a complex task that involves understanding the functions of its encoded proteins. While automated software for predicting protein function is widely used, it is prone to errors, with over 10% of automated annotations for bacterial enzymes and transporters being incorrect. Ideally, accurate annotations would allow us to predict a bacterium’s capabilities from its genome sequence, but in practice, this remains challenging. We describe interactive tools that infer potential capabilities from a genome sequence or that search a genome to find proteins that might perform a specific function of interest.
### Challenges in Predicting Bacterial Function
* Automated annotations are error-prone due to lack of knowledge of protein functions.
* Many proteins have vague or broad annotations that don’t provide specific insights into their roles or mechanisms.
* Only about a third of bacterial proteins are sufficiently similar to well-understood proteins for automated tools to predict their precise function.
### Interactive Tools for Predicting Protein Function
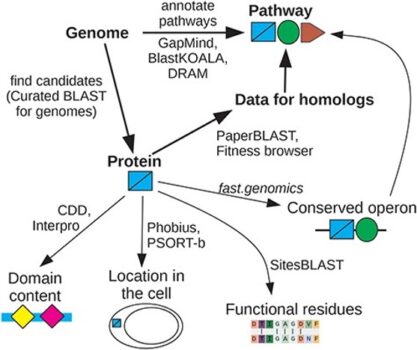
ENIGMA researchers have created interactive tools that quickly find different kinds of information relevant to a protein’s function, including:
* Papers about similar proteins
* Functional sites in similar proteins
* Conserved operons
* Mutant phenotypes
These tools can be accessed via PaperBLAST (http://papers.genomics.lbl.gov) and can often yield confident predictions of protein functions.
### Approaches for Predicting Bacterial Function
* **Comparative Genomics**: By comparing the genome of a bacterium with those of well-studied relatives, researchers can infer functions based on conserved genetic contexts.
* **Machine Learning Approaches**: Techniques like deep learning can be trained on large datasets to predict protein functions and metabolic capabilities.
### The Future of Predicting Bacterial Function
Predicting bacterial function from genomes is feasible but requires a multi-faceted approach, combining bioinformatics tools, experimental data, and literature review. As our understanding and tools evolve, so does our ability to accurately annotate and predict bacterial behavior from genomic sequences. This approach can significantly enhance our understanding of bacterial genomes and their functions.
## Key Takeaways
* Automated annotations of protein functions are error-prone and often incorrect.
* Interactive tools can be used to predict protein functions and infer potential capabilities from a genome sequence.
* A multi-faceted approach combining bioinformatics tools, experimental data, and literature review is required to accurately predict bacterial function from genomes.