Franco, L.C.; S. Steinbeisser, G.M. Zane, J.D. Wall, and M.W. Fields. 2018. Cr(VI) reduction and physiological toxicity are impacted by resource ratio in Desulfovibrio vulgaris. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 102:2839-2850 [doi]:1007/s00253-017-8724-4 {PMID}:29429007 PMCID:PMC5847207 OSTI:1420176
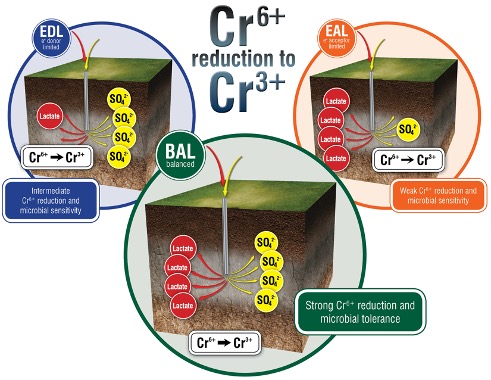
The presented study shows that resource ratio at different temperature has profound impacts on Cr(VI) reduction rates and Cr(VI) tolerance in Desulfovibrio vulgaris, a representative sulfate-reducing bacterium (SRB) studied for metal interactions. The increase in Cr(VI) toxicity for sulfate limited cells has implications for applications such as bioremediation where carbon and electron sources are injected into the subsurface, most likely creating an electron acceptor limited environment and thus promoting increased cellular toxicity. It is important to understand the growth characteristics of microorganisms that are capable of heavy metal immobilization, such as SRB, under typical field conditions to accurately assess and predict ability and rate of contaminant immobilization.
